Advanced RISC Machines

ARM-Based Processors
ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) architecture refers to a family of reduced instruction set computing (RISC) architectures for processors, renowned for their power efficiency. ARM processors are distinct from traditional x86 processors (from companies like Intel and AMD) due to their focus on lower power consumption, making them especially suitable for mobile devices, embedded systems, and increasingly, high-performance computing.
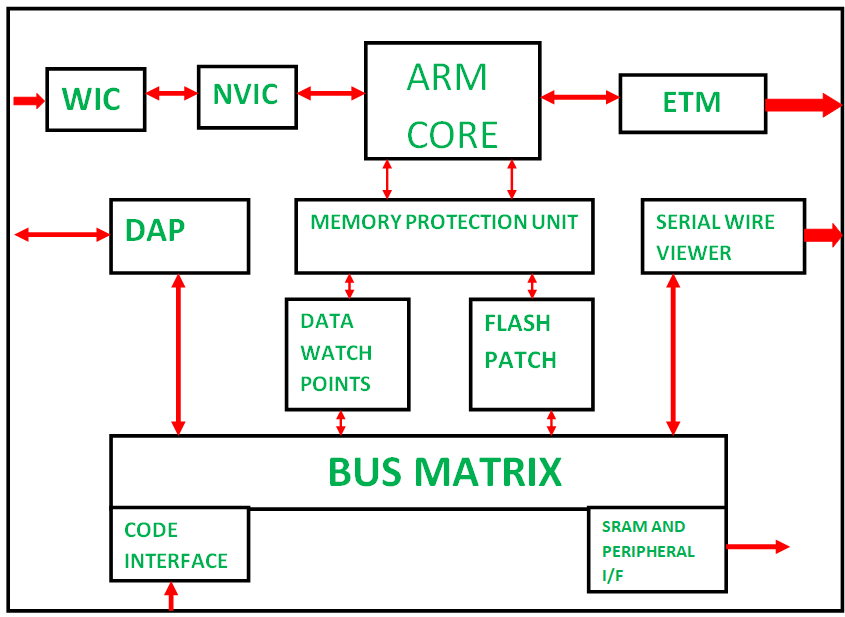
Key Features of ARM-Based Processors:
- Power Efficiency: ARM's RISC architecture simplifies instructions and requires fewer transistors compared to x86 designs. This results in lower power consumption and less heat, critical for battery-powered devices.
- Scalability: ARM processors are designed to scale across different uses, from tiny microcontrollers to powerful server CPUs. Companies can customize ARM architectures to suit their specific products.
- Customizability: Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) can license ARM architecture and create custom chips tailored for specific applications. Companies such as Qualcomm, Apple, and Samsung develop their system-on-chips (SoCs) based on ARM designs.
- Growing Ecosystem: ARM processors have an ever-expanding ecosystem, supporting various applications from smartphone computing to data center operations.
- High Performance Per Watt: The ARM architecture has evolved significantly, offering excellent performance for every watt of power consumed.

Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite: Evolution in ARM-Based Computing
Recently, Qualcomm introduced the Snapdragon X Elite processor as part of its foray into high-performance ARM-based chips targeted at laptops and PCs. This move attempts to challenge Apple’s M1/M2 chips and rival AMD/Intel laptop processors.
Snapdragon X Elite Features:
- CPU Design:
- The Snapdragon X Elite is likely to feature a multi-core design optimized for a blend of performance and power efficiency. Qualcomm might achieve this by grouping cores differently, similar to ARM’s "big.LITTLE" or "DynamIQ" designs, balancing high-performance cores with energy-efficient ones.
- Adreno GPU:
- Expected to include a powerful Adreno GPU, making it not only apt for general computing but also capable of handling graphics-intensive tasks and AI workloads.
- Advanced AI Engine:
- The Snapdragon X Elite is likely to have a dedicated AI engine. This is increasingly important as AI is being embedded into devices for tasks like real-time translation, computational photography, and other machine learning functionalities.
- 5G Connectivity:
- Snapdragon X Elite is anticipated to have integrated 5G capabilities, empowering laptops with always-on, high-speed connectivity—an attractive feature for business and mobile users.
- Efficient Manufacturing:
- Qualcomm typically utilizes advanced manufacturing processes, like 5nm or smaller, to produce more efficient and powerful chips with higher transistor density.
Performance Expectations:
Snapdragon X Elite aims to close the gap between ARM and x86 processors, particularly in several key areas:
- Multitasking & Performance: With more cores and an optimized architecture, it is expected to handle multitasking and CPU-intensive tasks efficiently. Qualcomm aims to match or surpass the performance of Intel’s i7/i9 and AMD’s Ryzen 7/9 series.
- Thermal Management: The ARM-based design focuses on thermal efficiency, ensuring sustained high-performance with lower heat dissipation, a common challenge for x86 chips in compact form factors such as ultra-thin laptops.
- AI and Machine Learning: Evolving from mobile prowess, Snapdragon X Elite is expected to handle AI workloads efficiently thanks to its dedicated AI capabilities, positioning it as a specialized processor for AI-driven tasks.

Future Scope:
With the evolution of ARM processors, a few trends are becoming clear in the industry:
1. Disruption in the PC Market:
- Apple has already shown the potential of ARM-based processors like the M1/M2 in high-performance computing. Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite could solidify ARM's presence in the PC market, providing more energy-efficient and potent alternatives to traditional x86 PCs.
2. Enterprise & Server Markets:
- ARM processors are making their way into the data center space, with companies like Amazon (AWS Graviton) and Microsoft testing ARM-based servers. Snapdragon X Elite could similarly branch into high-performance computing environments if it proves competitively capable.
3. Focus on AI & ML:
- With AI becoming increasingly common across industries, ARM processors with dedicated AI functionalities, like the Snapdragon X Elite, will find more applications in various devices and perhaps even reach autonomous vehicles, smart appliances, and consumer electronics.
4. Growing Presence in Laptops & Ultrabooks:
- Ultra-thin laptops benefit greatly from ARM's efficiency. Snapdragon X Elite and similar processors will likely spur a new generation of always-connected, ultra-light, long-battery-life devices.
5. Battery Life Enhancement:
- One of ARM’s key strengths is delivering extended battery performance compared to x86 processors. Snapdragon X Elite's adoption could see laptops with significantly longer battery life, a crucial selling point in modern laptops.
6. Expansion in Gaming & Content Creation:
- The inclusion of advanced GPUs and CPUs in ARM processors means they may soon tackle the domain of gaming and content creation, offering yet another alternative to existing x86-based systems.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite the promising future, certain challenges persist:
- Software Compatibility:
- While ARM-compatible software is growing, primarily with Windows support for ARM, there are still many legacy and specialized applications that rely on x86 architecture. It may take time for ARM to achieve software parity.
- Adoption Rates:
- Convincing both consumers and enterprises to move from well-known x86 platforms to ARM-based systems could be a slow and gradual process.
- Ecosystem Development:
- Building an extensive ecosystem that supports new hardware is crucial. Qualcomm will need to work closely with software developers and OEMs to ensure ecosystem maturity.
Conclusion
ARM-based processors are well-positioned to offer strong competition to the traditional x86 processors across various computing markets. With innovations like Qualcomm's Snapdragon X Elite, ARM is pushing the boundaries of performance while maintaining its edge in power efficiency. While challenges remain, the ongoing shift points toward a more ARM-dominated future, especially as the focus on mobile, energy-efficient, and AI-powered computing continues to grow.